Setting up a home network is a crucial step to ensure seamless connectivity and efficient sharing of resources among devices within your household. Whether for work, leisure, or communication, a well-organized home network simplifies digital living. In this guide, we’ll explore the step-by-step process and key components required on how to Set Up a home Network.
What is a Home Network?
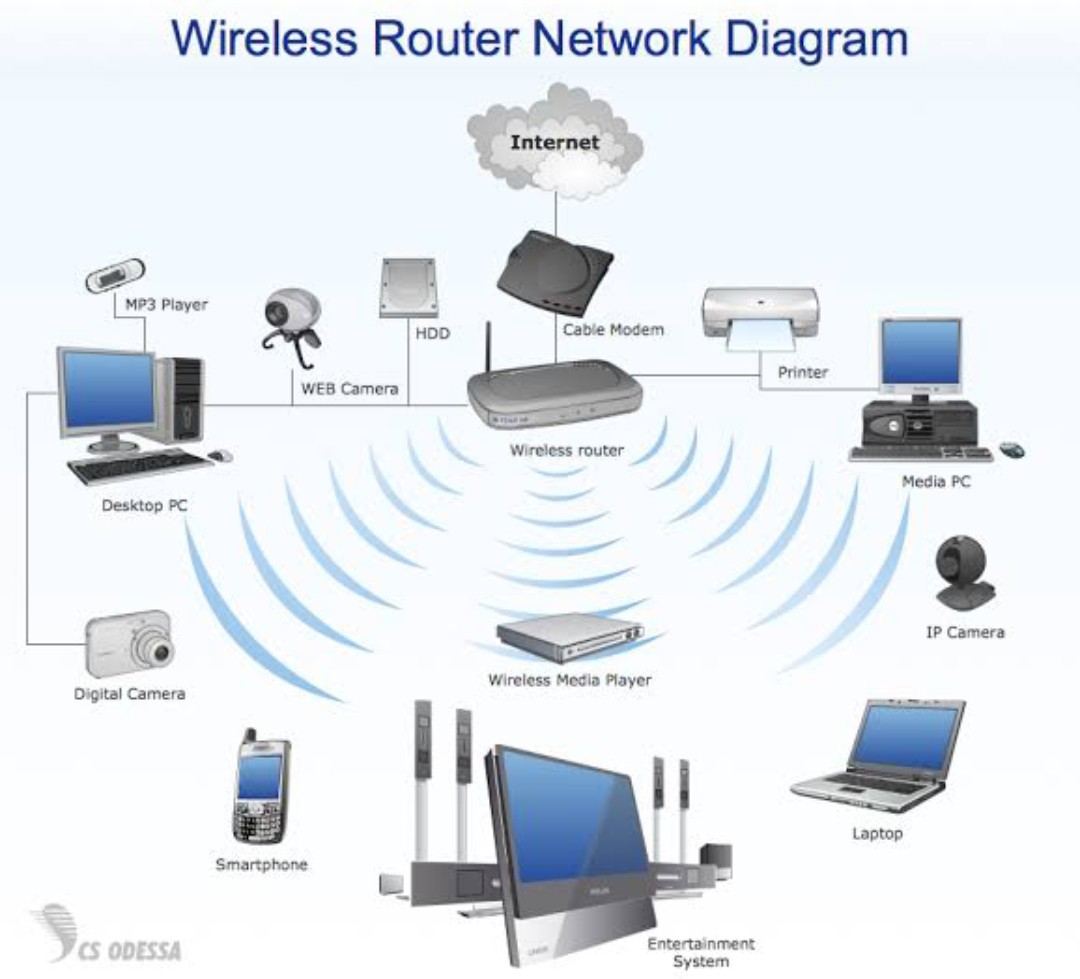
A home network is a collection of devices, such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and smart appliances, connected together to share resources and access the internet. It allows seamless communication and data exchange among these devices within the confines of your home. With a home network, you can enjoy benefits like file sharing, wireless printing, online gaming, streaming, and more.
It is a system that allows devices within a residence to communicate, share resources, and access the internet. It creates a local infrastructure connecting computers, smartphones, tablets, smart devices, and other gadgets, enabling seamless data transmission and sharing. The primary objective of a home network is to facilitate efficient communication and resource utilization among connected devices.
Key Components of Home Networks
1. Devices:
These include computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, gaming consoles, printers, and other connected appliances.
2. Router:
A fundamental component that directs data traffic between devices within the network and serves as the gateway to the internet.
3. Modem:
Connects to the internet service provider (ISP) network, enabling the network to access the internet.
4. Switches and Hubs:
Devices that facilitate connections between multiple wired devices in the network.
5. Access Points:
Devices that enable wireless communication, expanding the network’s reach and connectivity.
Basics of Home Networks
1. Local Area Network (LAN):
The network within your home is often referred to as a Local Area Network (LAN). It connects devices within a limited area, typically a single household.
2. Internet Service Provider (ISP):
An organization that provides internet access to homes and businesses. The ISP connects your home network to the wider internet.
3. IP Address:
Each device on a network is assigned a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address, allowing for identification and communication.
4. Wi-Fi and Ethernet:
Home networks can be either wired (Ethernet) or wireless (Wi-Fi). Wi-Fi allows for convenient and mobile connectivity, while Ethernet offers faster and more stable connections.
5. Security Measures:
Implementing security protocols, such as encryption and passwords, is essential to protect your home network from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
It is important to note that these basics lays the foundation for setting up an efficient and secure home network. From connecting devices to ensuring network security, comprehending these fundamental concepts will help you optimize your home network effectively.
Types of Home Networks
Home networks come in various forms, each catering to different connectivity needs and preferences. Depending on the size of the residence, the number of devices, and the desired coverage, different types of home networks may be suitable. Here are the main types:
1. Wired Home Networks
Ethernet:
- Uses Ethernet cables to connect devices directly to the network.
- Provides faster and more reliable connections compared to wireless networks.
- Ideal for stationary devices like computers, gaming consoles, and smart TVs.
Powerline:
- Uses existing electrical wiring to transmit data signals.
- Suitable for locations where running Ethernet cables is impractical.
- Offers a compromise between speed and convenience.
2. Wireless Home Networks
Wi-Fi:
- Most common type, utilizing radio waves to connect devices wirelessly.
- Provides mobility and flexibility, allowing users to access the network from anywhere within the coverage area.
- Ideal for smartphones, tablets, laptops, and IoT devices.
3. Hybrid Home Networks
Wired/Wireless Combo:
- Combines wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi) connections.
- Maximizes the benefits of both technologies, offering reliability and flexibility.
- Wired connections for stationary devices and wireless for mobile ones.
4. Mesh Networks
Mesh Wi-Fi:
- Consists of multiple interconnected nodes or access points.
- Ensures consistent Wi-Fi coverage across a larger area or multi-story homes.
- Each node communicates with the others, creating a seamless network.
5. Mobile Hotspots
Cellular Networks:
- Utilizes cellular data networks to provide internet connectivity.
- Useful when a traditional home network is unavailable or as a backup option.
6. Satellite Internet Networks
Satellite Internet:
- Connects to the internet via a satellite dish.
- Suitable for rural or remote areas with limited traditional internet access.
When you understand the types of home networks helps in choosing the most suitable setup based on factors like the size of your home, the number of devices you have, and your internet usage requirements. Whether you prioritize speed, mobility, or coverage, there’s a home network type to meet your specific needs.
How to Set Up a Home Network
Setting up a home network may seem overwhelming, but breaking it down into steps simplifies the process. Follow these steps to establish a reliable and efficient home network.
1. Assess Your Network Needs
- Determine Device Count: Estimate the number of devices that will connect to the network to ensure your router can handle the load.
- Evaluate Space: Consider the size of your residence to decide the type and number of access points needed for adequate coverage.
2. Choose the Right Router
- Select Router Type: Choose between single, dual, or tri-band routers based on your internet usage and device count.
- Consider Speed and Range: Opt for routers with appropriate speed (measured in Mbps or Gbps) and sufficient coverage range for your home.
- Check for Advanced Features: Look for features like Quality of Service (QoS), guest network, and parental controls to enhance security and performance.
3. Connect Your Modem
- Power Off Modem: Turn off your modem and unplug it from the power source.
- Connect Router: Use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem’s Ethernet port to the WAN or Internet port on the router.
- Power On Modem: Plug the modem back in and turn it on. Wait for it to fully boot up.
4. Configure Your Router
- Access Router Settings: Enter the router’s IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1) into a web browser and log in using the default credentials or as provided by the manufacturer.
- Set Network Name (SSID) and Password: Change the default SSID and set a strong, unique password for your Wi-Fi network.
- Enable Encryption: Enable WPA3 or WPA2 encryption to secure your Wi-Fi network.
5. Set Up Wi-Fi and Devices
- Connect Devices: Access the Wi-Fi settings on each device, select your network, and enter the Wi-Fi password.
- Connect Wired Devices: Use Ethernet cables to connect devices directly to the router or switch.
6. Optimize Your Network
- Position the Router: Place the router in a central location for even coverage throughout your home.
- Update Firmware: Check for router firmware updates and apply them to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Manage Bandwidth: Configure Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize critical applications and devices.
7. Secure Your Network
- Change Default Passwords: Change the default router login credentials to enhance security.
- Use Guest Network: Enable a separate guest network to keep your main network secure.
- Regularly Update Security: Update your router’s security settings and firmware to protect against vulnerabilities.
8. Expand Your Network (if needed)
- Add Access Points: Consider adding additional access points or Wi-Fi extenders for larger homes or areas with weak coverage.
Follow these steps to set up a robust home network that meets your connectivity needs and provides a seamless internet experience for all your devices.
Network Security Measures
Ensuring the security of your home network is paramount to protect your sensitive data and maintain privacy. Implement these network security measures to create a robust defense against potential threats.
1. Change Default Router Login Credentials
- Change Passwords: Change the default login username and password for your router to unique, strong credentials.
- Avoid Defaults: Avoid using easily guessable passwords like “admin” or “password” to enhance security.
2. Enable Network Encryption
- WPA3/WPA2 Encryption: Enable WPA3 or WPA2 encryption on your Wi-Fi network to secure data transmission.
- Avoid WEP: Avoid using WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption as it’s outdated and easily penetrable.
3. Set Up a Guest Network
- Isolate Guest Devices: Enable a separate guest network to isolate guest devices from your main network, enhancing security.
- Limit Access: Set time or device access limits for guest networks to prevent abuse.
4. Regularly Update Router Firmware
- Check for Updates: Routinely check for firmware updates for your router and install them to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates to ensure your router is always equipped with the latest security enhancements.
5. Enable a Firewall
- Activate Built-in Firewall: Enable the firewall provided by your router to filter incoming and outgoing traffic, protecting against unauthorized access.
- Customize Firewall Rules: Configure specific firewall rules to allow or block certain types of traffic based on your preferences.
6. MAC Address Filtering
- Permit Specific Devices: Only allow devices with approved MAC addresses to connect to your network, enhancing control and security.
- Regularly Update List: Update the list of permitted MAC addresses when adding or removing devices from your network.
7. Use Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Secure Remote Access: Use a VPN to encrypt data and provide a secure connection when accessing your home network remotely.
- Choose Reliable VPN Providers: Opt for reputable VPN services with strong encryption and a no-logs policy.
8. Regularly Monitor Network Activity
- Check Device Connections: Periodically review connected devices to ensure only authorized devices are accessing the network.
- Analyze Router Logs: Monitor router logs for suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts.
9. Secure IoT Devices
- Change Default IoT Device Passwords: Change default passwords on IoT devices to prevent unauthorized access.
- Segment IoT Devices: Create a separate network for IoT devices to minimize potential security risks to your main network.
10. Educate Family Members
- Security Awareness: Educate all family members about network security best practices, emphasizing the importance of strong passwords and safe browsing habits.
When you implement these network security measures, you can significantly enhance the security of your home network, keeping your data safe and maintaining a secure online environment for all users. Stay vigilant and proactive in securing your network against evolving cyber threats.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance of Home Networks
Regular troubleshooting and maintenance are crucial to ensure your home network functions efficiently and stays secure. Follow these steps to troubleshoot common issues and maintain the health of your home network.
Troubleshooting Home Network Issues
1. Check Network Status
- Restart Devices: Restart your modem, router, and connected devices to resolve temporary network glitches.
- Check LEDs: Inspect router LEDs to ensure they indicate a stable connection.
2. Verify Device Connectivity
- Ping Test: Use the command prompt to ping a website or IP address to check for connectivity.
- Check Wired Connections: Ensure Ethernet cables are securely connected and not damaged.
- Check Wi-Fi Signal: Ensure devices are within the router’s coverage range for optimal Wi-Fi signal strength.
3. Review Router Settings
- Check Configuration: Review router settings to ensure they are configured correctly, especially after any firmware updates.
- Reconfigure if Necessary: Adjust Wi-Fi channels or security settings if you experience interference or suspect a security breach.
4. Secure Network
- Update Passwords: Regularly change Wi-Fi passwords and router login credentials to enhance security.
- Monitor Connected Devices: Check the list of connected devices to ensure no unauthorized access.
5. Check for Interference
- Identify Interference Sources: Identify and eliminate potential interference sources like other electronic devices or neighboring networks on the same Wi-Fi channel.
- Optimize Router Placement: Reposition your router to minimize interference and maximize coverage.
Network Maintenance Tips
1. Regularly Update Firmware
- Check for Updates: Routinely check for and install firmware updates for your router to improve performance and security.
- Automate Updates: Enable automatic updates to ensure your router is always running the latest software.
2. Perform Speed Tests
- Check Internet Speed: Regularly conduct internet speed tests to ensure you’re receiving the expected speed from your ISP.
- Contact ISP if Necessary: If you consistently experience slow speeds, contact your internet service provider for assistance.
3. Backup Router Configuration
- Save Settings: Backup your router’s configuration settings to quickly restore them in case of a reset or hardware failure.
4. Monitor Data Usage
- Check Bandwidth Usage: Monitor your monthly bandwidth usage to ensure you stay within your plan limits.
- Manage Data Consumption: Limit heavy data usage activities during peak hours to maintain optimal performance.
5. Regularly Clean and Ventilate Equipment
- Dust Removal: Clean your router and other networking equipment regularly to prevent dust accumulation, which can affect performance.
- Ventilation: Ensure networking equipment is well-ventilated to prevent overheating.
By regularly troubleshooting issues and following these maintenance tips, you can ensure your home network runs smoothly, providing reliable connectivity for all your devices. Stay proactive in maintaining your network to enjoy a seamless online experience.
Optimizing Home Network Performance

Optimizing your home network performance is essential to ensure a fast, reliable, and seamless connection. Follow these steps to enhance your network’s efficiency and enjoy an optimal online experience.
1. Upgrade Your Router
- Dual or Tri-Band Routers: Upgrade to a dual or tri-band router to separate devices and reduce congestion, especially in a multi-device household.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): Consider upgrading to Wi-Fi 6 for higher speeds, increased capacity, and improved performance, especially with newer devices that support this standard.
2. Position Your Router Strategically
- Central Location: Place your router in a central location within your home for even coverage.
- Elevate the Router: Position the router at an elevated point to improve signal dispersion.
- Minimize Obstructions: Keep the router away from walls, metal surfaces, and other obstructions that may hinder Wi-Fi signals.
3. Manage Bandwidth Effectively
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritize specific applications and devices to ensure critical activities (e.g., work-related tasks) get ample bandwidth.
- Traffic Shaping: Configure traffic shaping to manage traffic flow and allocate bandwidth effectively.
4. Optimize Wi-Fi Settings
- Choose the Right Channel: Select the least congested Wi-Fi channel to minimize interference and improve speed.
- Adjust Transmit Power: Fine-tune the transmit power of your router to balance coverage and performance based on your home’s size.
- Enable Beamforming: Enable beamforming to focus Wi-Fi signals towards connected devices, enhancing overall performance.
5. Use Ethernet Where Possible
- Wired Connections: Utilize Ethernet cables to connect stationary devices like computers, gaming consoles, or smart TVs for faster and more reliable connectivity.
- Powerline Adapters: Consider powerline adapters to provide a wired-like connection using existing electrical wiring.
6. Regularly Update Firmware and Devices
- Router Firmware: Ensure your router’s firmware is up to date to benefit from the latest features, security enhancements, and bug fixes.
- Device Updates: Regularly update all devices connected to the network (computers, smartphones, etc.) to ensure optimal performance and security.
7. Consider Network Expansion
- Wi-Fi Extenders/Repeaters: Use Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters to amplify signals and extend coverage to areas with weak connectivity.
- Mesh Networking: Invest in a mesh Wi-Fi system for seamless, consistent coverage across your entire home.
8. Monitor Network Performance
- Use Network Monitoring Tools: Utilize network monitoring applications to track performance, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues.
- Regularly Check Speeds: Conduct speed tests using reliable online platforms to monitor your network’s performance.
By implementing these optimization techniques, you can significantly enhance your home network’s performance, ensuring a smooth and efficient connectivity experience for all your devices. Stay proactive and tailor your network to your specific needs for the best results.
Creating Network Storage and Sharing
Setting up network storage and sharing capabilities allows you to centralize files, access them from multiple devices, and collaborate seamlessly. Follow these steps to create an efficient network storage system.
1. Choose a Network Storage Solution
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): Invest in a NAS device, a dedicated storage server connected to your network, to store and access files securely.
- Personal Cloud Storage: Utilize cloud storage services that allow you to create a personal cloud accessible via the internet.
- External Hard Drives: Connect external hard drives to your router or a computer to set up network-attached storage.
2. Set Up Your Storage Device
- Connect and Configure: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to connect and configure your chosen storage device.
- Create User Accounts: Establish user accounts with unique credentials to control access and permissions.
3. Organize and Categorize Your Files
- Create Folders and Categories: Organize your files into folders based on type, project, or user to streamline access and retrieval.
- Use Naming Conventions: Adopt a consistent naming convention for files and folders to enhance searchability.
MUST READ: Fix a computer keyboard not working with these steps
4. Enable Remote Access
- VPN Setup: If using a NAS, configure a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to allow secure remote access to your files.
- Cloud Storage Apps: For cloud-based solutions, install relevant apps on your devices to access files on the go.
5. Implement Access Controls and Permissions
- Assign Permissions: Define access levels (read, write, delete) for users or groups to control who can access and modify specific files and folders.
- Role-Based Access: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure users have appropriate permissions based on their roles.
6. Enable File Sharing
- Generate Share Links: For cloud-based solutions, generate shareable links to specific files or folders to collaborate with others.
- Set Expiry and Access Limits: Customize sharing settings, including expiration dates and access permissions, to manage sharing effectively.
7. Backup Your Data
- Scheduled Backups: Set up automated backups to ensure your data is safely stored and can be restored in case of loss.
- Offsite Backups: Consider backing up critical data to an offsite location or a cloud-based backup service for added security.
8. Regularly Review and Update
- Review Access and Permissions: Periodically audit access rights to ensure they align with current requirements.
- Optimize File Organization: Evaluate and adjust the folder structure and naming conventions as needed for improved efficiency.
By following these steps, you can create an organized, secure, and easily accessible network storage system. Whether using a NAS, cloud-based solution, or external hard drives, efficient file sharing and collaboration are at your fingertips.
Guest Network Setup: Providing Secure Connectivity for Guests
Setting up a guest network is a smart way to offer internet access to visitors while maintaining the security and privacy of your main network. Follow these steps to set up a guest network securely.
1. Access Your Router Settings
- Access Router Interface: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address (usually something like 192.168.1.1) to access the router’s settings.
- Login: Log in using your router’s username and password.
2. Enable Guest Network Feature
- Locate Guest Network Settings: Navigate to the Wi-Fi or Guest Network settings section of your router’s interface.
- Enable Guest Network: Toggle the guest network feature on.
3. Configure Guest Network Settings
- Set Network Name (SSID): Create a unique name (SSID) for the guest network to differentiate it from your main network.
- Set Encryption and Password: Choose an encryption method (WPA2/WPA3) and set a password for the guest network.
4. Isolate Guest Network from Main Network
- Enable Network Isolation: Ensure that devices on the guest network cannot communicate with devices on the main network for added security and privacy.
5. Limit Guest Network Access
- Set Time and Usage Limits: Configure restrictions on how long a guest can stay connected or limit their bandwidth usage.
- Schedule Guest Network Availability: Set specific times when the guest network is available to control usage.
6. Apply Security Measures
- Captive Portal and Terms of Use: Implement a captive portal where guests must agree to terms of use before accessing the network.
- Enable MAC Address Filtering: Use MAC address filtering to allow only authorized devices to connect to the guest network.
7. Regularly Review Guest Network Usage
- Monitor Devices: Check the devices connected to the guest network to ensure there are no unauthorized users.
- Audit Security Settings: Periodically review and update the security settings of the guest network.
8. Educate Guests on Network Usage
- Provide Network Information: Share the guest network name (SSID) and password with your guests.
- Explain Terms of Use: Inform guests about any terms of use or restrictions in place for the guest network.
By setting up a guest network following these steps, you offer a secure and separate connectivity option for your guests, enhancing both convenience and security within your home network.
Smart Home Integration
Integrating smart devices into your home network allows for a more convenient, efficient, and connected living experience. Follow these steps to seamlessly integrate smart home devices into your network.
1. Select Smart Devices Compatible with Your Network
- Research Compatibility: Ensure that the smart devices you choose are compatible with your existing home network (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, etc.).
- Check Protocols: Verify that the devices use standard communication protocols compatible with your network.
2. Install and Configure Smart Home Hub (if applicable)
- Choose a Hub: If using a smart home hub, select one that is compatible with a variety of devices.
- Follow Setup Instructions: Install and configure the hub as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Connect Devices to Your Network
- Download Companion Apps: Download the respective mobile apps for each smart device from the app store.
- Follow Device Setup Instructions: Follow the device-specific setup instructions in the app to connect them to your Wi-Fi network.
4. Organize Devices into Rooms or Zones
- Categorize Devices: Organize devices into rooms or zones (e.g., living room, kitchen) within the app to manage them efficiently.
- Assign Names: Assign names to each device to easily identify and control them.
5. Create Automation and Scenes
- Define Automation Rules: Set up automation rules (e.g., turn off lights when no motion detected) to streamline device interactions.
- Create Scenes: Define scenes (e.g., “Good Morning”) that trigger multiple devices to perform specific actions simultaneously.
6. Establish Voice Control (Optional)
- Integrate Voice Assistants: If desired, integrate voice assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant to control smart devices using voice commands.
- Link Accounts: Link your smart home accounts with the voice assistant app for seamless voice control.
7. Ensure Security and Privacy
- Update Firmware: Regularly update firmware for smart devices to address security vulnerabilities.
- Secure Network: Ensure your Wi-Fi network is secure to protect sensitive data shared by smart devices.
8. Regularly Review and Update Settings
- Check Device Performance: Periodically review device performance and troubleshoot any issues.
- Update Automation: Modify and optimize automation rules and scenes based on changing needs.
By following these steps, you can seamlessly integrate smart devices into your home network, creating a connected and efficient living environment. Enjoy the convenience and enhanced lifestyle that smart home integration brings.
Remote Access and VPN Setup: Securely Accessing Your Home Network Remotely
Setting up remote access and a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for your home network allows you to access your devices and data securely from anywhere. Follow these steps to set up remote access and a VPN..
1. Understand Remote Access and VPN
- Remote Access: Remote access allows you to access your devices and network from a location outside your home.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel over the internet, ensuring secure communication between your device and the home network.
2. Configure Remote Access on Devices
- Enable Remote Access Features: Many routers and devices have built-in remote access features. Enable these within the device’s settings.
- Create User Accounts: Set up user accounts with strong passwords for secure access.
3. Configure Router for Remote Access
- Port Forwarding: Configure port forwarding on your router to allow access to specific services or devices from outside your network.
- Dynamic DNS: Set up Dynamic DNS (DDNS) to assign a domain name to your home network, even if your ISP assigns a dynamic IP address.
4. Select and Set Up a VPN Service
- Choose a VPN Provider: Select a reputable VPN service that meets your requirements for security, speed, and accessibility.
- Sign Up and Install: Sign up for the VPN service and install the VPN client on your devices.
5. Configure VPN on Your Router
- Router Compatibility: Ensure your router supports VPN integration. Not all routers have this capability.
- Follow VPN Provider Instructions: Follow the VPN provider’s instructions to configure the VPN on your router.
6. Access Devices Remotely via VPN
- Connect to VPN: Use the VPN client to connect securely to your home network from any remote location.
- Access Devices: Access your devices as if you were at home, securely and privately through the VPN.
7. Maintain Security and Privacy
- Regularly Update VPN Software: Ensure your VPN software is up to date to benefit from the latest security features.
- Use Strong Authentication: Utilize strong authentication methods, like two-factor authentication (2FA), to enhance security.
8. Test and Troubleshoot
- Test Remote Access: Conduct tests to ensure remote access and VPN are working as expected.
- Troubleshoot Issues: If you encounter issues, refer to the VPN provider’s troubleshooting guides or contact their support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, setting up a home network is a fundamental step towards a connected and efficient living space. Starting from choosing the right network equipment to configuring it effectively, this process involves organizing devices, ensuring security measures, and integrating smart home devices seamlessly.
As technology advances, understanding how to set up a home network becomes increasingly crucial, not only for convenience but also for privacy and security. By following the appropriate steps and staying informed about the latest advancements, you can create a robust home network tailored to your needs, enhancing your digital lifestyle and enabling a smooth flow of information within your home.
